Welcome, curious minds, to a journey through the evolution of Material Requirements Planning (MRP) to Manufacturing Resource Planning (MRP II) and beyond. In the ever-evolving landscape of manufacturing, the need for efficient planning and resource utilization has been a constant challenge. From its humble beginnings as a way to calculate materials needed for production, MRP has transformed into a comprehensive system that encompasses not just materials, but also production scheduling, labor management, and supply chain optimization. Join us as we explore how MRP has adapted to meet the demands of modern manufacturing in this age of Industry 4.0.
Historical Origins of MRP Systems
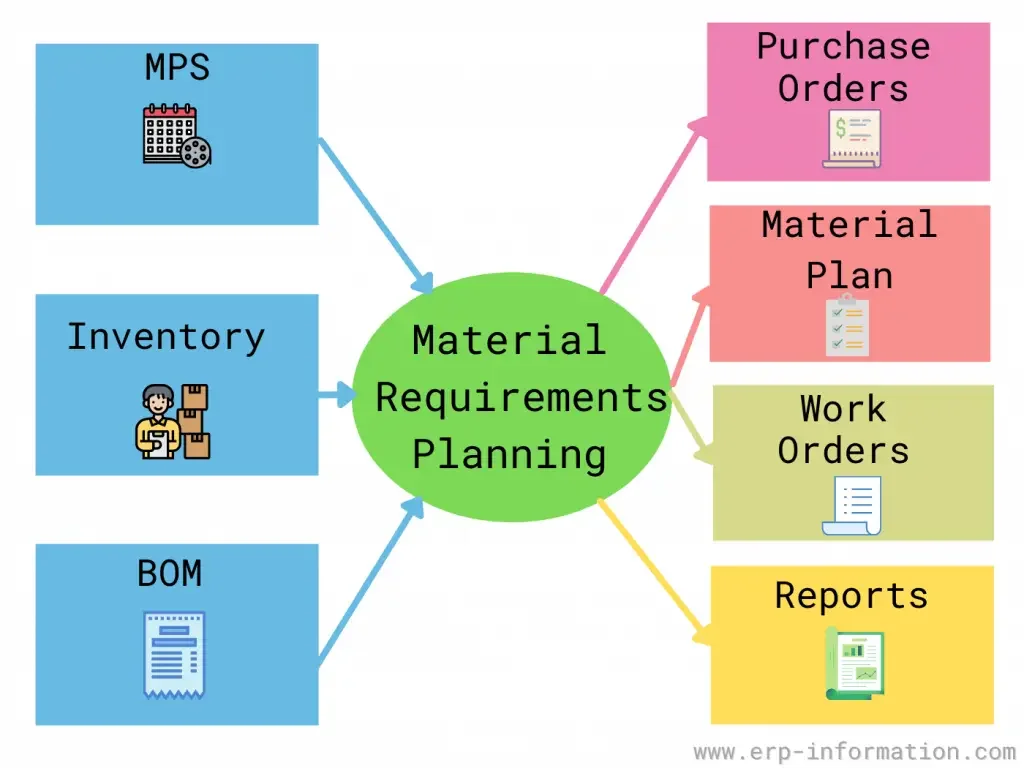
MRP, or Material Requirements Planning, is a system that is used in manufacturing industries to plan and manage the materials needed to produce goods. The origins of MRP can be traced back to the 1960s when the concept of computer-based planning and scheduling first emerged. At that time, companies were struggling with inventory control and production planning due to manual processes that were time-consuming and prone to errors.
One of the key pioneers in the evolution of MRP systems was Joseph Orlicky, who is often referred to as the father of MRP. Orlicky was a former IBM engineer who developed the first MRP system while working at a manufacturing company in the 1960s. He recognized the need for a more efficient way to plan and manage materials in order to improve production processes and reduce costs.
Orlicky’s groundbreaking work laid the foundation for what would later become known as Material Requirements Planning. The first MRP systems were developed in the 1970s and were primarily used by large manufacturing companies such as IBM, Ford, and General Motors. These early systems were based on complex algorithms that calculated material requirements based on demand forecasts, lead times, and inventory levels.
Over the years, MRP systems have evolved to become more sophisticated and user-friendly. The introduction of MRP II, or Manufacturing Resource Planning, in the 1980s integrated other functions such as capacity planning, production scheduling, and financial management into the system. This allowed companies to have a more comprehensive view of their operations and make more informed decisions.
With the advancement of technology, MRP systems have become even more powerful and flexible. Modern MRP systems are now cloud-based, allowing for real-time data access and collaboration among different departments within an organization. They also incorporate artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms to improve forecasting accuracy and optimize production processes.
Today, MRP systems are an essential tool for manufacturers around the world to streamline their operations, reduce costs, and improve overall efficiency. They have come a long way since their humble beginnings in the 1960s and continue to evolve to meet the ever-changing needs of the industry.
Advantages of Modern MRP Technology
Modern Material Requirements Planning (MRP) technology has revolutionized the way businesses manage their inventory and production processes. With the advancements in technology, MRP systems have become more sophisticated and user-friendly, allowing companies to streamline their operations and increase efficiency. Here are some key advantages of modern MRP technology:
1. Enhanced visibility and transparency: One of the biggest advantages of modern MRP technology is the enhanced visibility it provides into the supply chain. With real-time data and analytics, companies can now track their inventory levels, production schedules, and order fulfillment processes with unprecedented accuracy. This increased visibility allows businesses to make more informed decisions and proactively address any potential issues before they become a problem.
2. Improved collaboration and communication: Modern MRP systems are designed to facilitate collaboration and communication between different departments within an organization. By centralizing all relevant information in one place, employees can easily access the data they need to make informed decisions and coordinate activities across departments. This improved communication and collaboration can help reduce lead times, minimize delays, and improve overall efficiency.
3. Automated workflows and processes: Another key advantage of modern MRP technology is the ability to automate repetitive tasks and processes. By setting up workflows and triggers within the system, companies can eliminate manual data entry, reduce errors, and speed up production cycles. This automation not only saves time and resources but also allows employees to focus on more strategic tasks that drive business growth.
4. Scalability and flexibility: Modern MRP systems are highly scalable and flexible, allowing businesses to adapt to changing market conditions and scale their operations as needed. Whether a company is experiencing rapid growth or facing unexpected challenges, a modern MRP system can easily accommodate fluctuations in demand, inventory levels, and production schedules. This scalability and flexibility make modern MRP technology a valuable asset for businesses of all sizes.
5. Cost savings and efficiency: Ultimately, the goal of modern MRP technology is to help businesses save costs and improve efficiency. By optimizing inventory levels, production schedules, and order fulfillment processes, companies can reduce waste, minimize lead times, and maximize resource utilization. This increased efficiency not only lowers operating costs but also enhances customer satisfaction and competitive advantage in the market.
In conclusion, the evolution of MRP technology has brought about numerous advantages for businesses looking to streamline their operations and improve efficiency. From enhanced visibility and communication to automated workflows and cost savings, modern MRP technology offers a wide range of benefits that can help companies stay competitive in today’s fast-paced business environment.
Challenges Faced by Early MRP Systems
As Material Requirements Planning (MRP) systems began to evolve, they faced various challenges that hindered their effectiveness in the early stages. One major challenge was the lack of technology and computing power available at the time. In the early days of MRP, computers were bulky, expensive, and not equipped to handle the complex calculations required for efficient material planning. This limited the capabilities of early MRP systems and made them slow and error-prone.
Another challenge faced by early MRP systems was the lack of standardized data formats and communication protocols. Without a common language for sharing information between different departments and suppliers, MRP systems struggled to accurately track inventory levels, lead times, and production schedules. This lack of interoperability made it difficult for businesses to coordinate their materials planning processes effectively.
Additionally, early MRP systems often lacked real-time data updates, relying instead on manual inputs and periodic reports. This meant that planners were working with outdated information, leading to inaccuracies in demand forecasts and inventory management. Without up-to-date information, companies struggled to make timely decisions and respond quickly to changes in demand or supply chain disruptions.
Furthermore, the complexity of early MRP systems posed a challenge for many businesses, as they required specialized training and expertise to operate effectively. Implementing and maintaining an MRP system was costly and time-consuming, and many companies lacked the resources and knowledge to fully leverage the capabilities of these systems. This resulted in suboptimal performance and limited the potential benefits that MRP could offer.
Lastly, early MRP systems often faced resistance from employees who were accustomed to manual planning processes. The shift to computerized systems represented a significant change in workflow and required employees to adapt to new ways of working. This resistance to change, coupled with the challenges of implementing and integrating MRP systems into existing business processes, created barriers to adoption and hindered the successful implementation of MRP in many organizations.
The Impact of Industry 4.0 on MRP Evolution
Industry 4.0, also known as the Fourth Industrial Revolution, is the current trend of automation and data exchange in manufacturing technologies. This revolution is characterized by the integration of cyber-physical systems, the Internet of Things (IoT), and cloud computing in manufacturing processes. The impact of Industry 4.0 on Material Requirements Planning (MRP) has been significant, leading to the evolution and adaptation of MRP systems to meet the demands of modern manufacturing environments.
One of the key ways in which Industry 4.0 has influenced the evolution of MRP is through the incorporation of real-time data and analytics. With the rise of IoT devices and sensors in manufacturing equipment, MRP systems can now access real-time data on inventory levels, production progress, and demand forecasts. This real-time data allows MRP systems to make more accurate and timely decisions, leading to improved efficiency and cost savings for manufacturers.
Furthermore, Industry 4.0 has enabled the implementation of smart MRP systems that can autonomously adjust production schedules and material orders based on changing demand patterns. These smart MRP systems use advanced algorithms and machine learning capabilities to analyze data and predict future demand, allowing manufacturers to optimize their production processes and respond quickly to market changes.
Another significant impact of Industry 4.0 on MRP evolution is the increased connectivity and integration of manufacturing processes. With the advent of cyber-physical systems, MRP systems can now communicate with other systems and devices on the manufacturing floor, such as robotics, 3D printers, and automated guided vehicles. This level of connectivity enables a seamless flow of information and materials throughout the production process, leading to reduced lead times and improved overall efficiency.
Additionally, Industry 4.0 has facilitated the development of cloud-based MRP systems that offer enhanced flexibility and scalability for manufacturers. Cloud-based MRP systems store data in the cloud, allowing manufacturers to access their MRP system from anywhere at any time. This flexibility enables manufacturers to adapt to changing market conditions and scale their operations more easily, without the need for expensive hardware installations or upgrades.
In conclusion, Industry 4.0 has had a profound impact on the evolution of MRP systems, leading to the development of more advanced, efficient, and flexible solutions for modern manufacturing environments. By incorporating real-time data, smart algorithms, enhanced connectivity, and cloud-based technologies, MRP systems are better equipped to meet the challenges of today’s fast-paced and data-driven manufacturing industry.
Future Trends in MRP Development
As technology continues to advance at a rapid pace, the field of Material Requirements Planning (MRP) is also evolving to meet the changing needs of businesses. In the future, we can expect to see a number of exciting trends in MRP development that will revolutionize the way companies manage their inventory and production processes.
One of the most significant trends in MRP development is the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning. These technologies have the potential to vastly improve the accuracy and efficiency of MRP systems by analyzing vast amounts of data and making real-time adjustments to production schedules and inventory levels. By using AI and machine learning, companies can optimize their supply chains, reduce costs, and improve overall performance.
Another important trend in MRP development is the move towards cloud-based systems. Cloud-based MRP solutions offer several advantages over traditional on-premise systems, including greater scalability, flexibility, and accessibility. With a cloud-based MRP system, companies can access their data from anywhere, at any time, and can easily scale their system up or down based on their changing needs. This flexibility is particularly important for small and medium-sized businesses that may not have the resources to invest in expensive on-premise systems.
Blockchain technology is also poised to play a role in the future of MRP development. By using a secure, decentralized ledger to track the movement of goods and materials through the supply chain, companies can reduce the risk of fraud, improve transparency, and ensure the authenticity of their products. Blockchain technology has the potential to revolutionize the way companies track and trace their inventory, leading to greater efficiency and trust in the supply chain.
Another trend to watch in MRP development is the rise of mobile applications. With the increasing use of smartphones and tablets in the workplace, companies are turning to mobile MRP apps to improve the efficiency of their operations. These apps allow employees to access MRP data on the go, make real-time updates to production schedules, and receive alerts and notifications about inventory levels. By using mobile MRP apps, companies can streamline their operations, improve communication, and make faster, more informed decisions.
Finally, sustainability and environmental concerns are becoming increasingly important in MRP development. As companies strive to reduce their carbon footprint and minimize waste, they are looking for MRP systems that can help them achieve their sustainability goals. In the future, we can expect to see MRP systems that are designed to optimize production processes, minimize energy consumption, and reduce waste. By incorporating sustainability principles into MRP development, companies can not only improve their environmental impact but also create a more efficient and cost-effective supply chain.
In conclusion, the future of MRP development holds many exciting possibilities. From the integration of AI and machine learning to the adoption of cloud-based systems, blockchain technology, mobile applications, and sustainability principles, the field of MRP is evolving to meet the needs of modern businesses. By staying ahead of these trends and embracing new technologies, companies can revolutionize their supply chain management and achieve greater efficiency, transparency, and sustainability in their operations.